About Vagustim
Vagustim is the world’s first multi-purpose, smart, non-invasive bilateral auricular vagus nerve stimulation device. Vagustim Stimulator is controlled by its Mobile App and the stimulation parameters of Vagustim are adjustable.

Vagus Nerve Stimulation
Since the vagus nerve is the biggest part of the parasympathetic nervous system, stimulation of the vagus nerve may increase the activity of the parasympathetic nervous system. Through this process, the autonomic nervous system balance can be restored and the disorders related to the dysfunction can be eliminated.
The autonomic nervous system dysfunction may cause chronic pains, gastrointestinal disorders, cardiac problems, sleep disorders, depression, anxiety, and many other diseases/disorders *.
* Özden, A.V. (2024). Vagus Nerve Stimulation in Peripheral Targets. In: Frasch, M.G., Porges, E.C. (eds) Vagus Nerve Stimulation . Neuromethods, vol 205. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3465-3_1
Our Mission
We are committed to developing cutting-edge, high-quality Bioelectronic Medicine devices and medical solutions by utilizing the power of Non-invasive Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS).
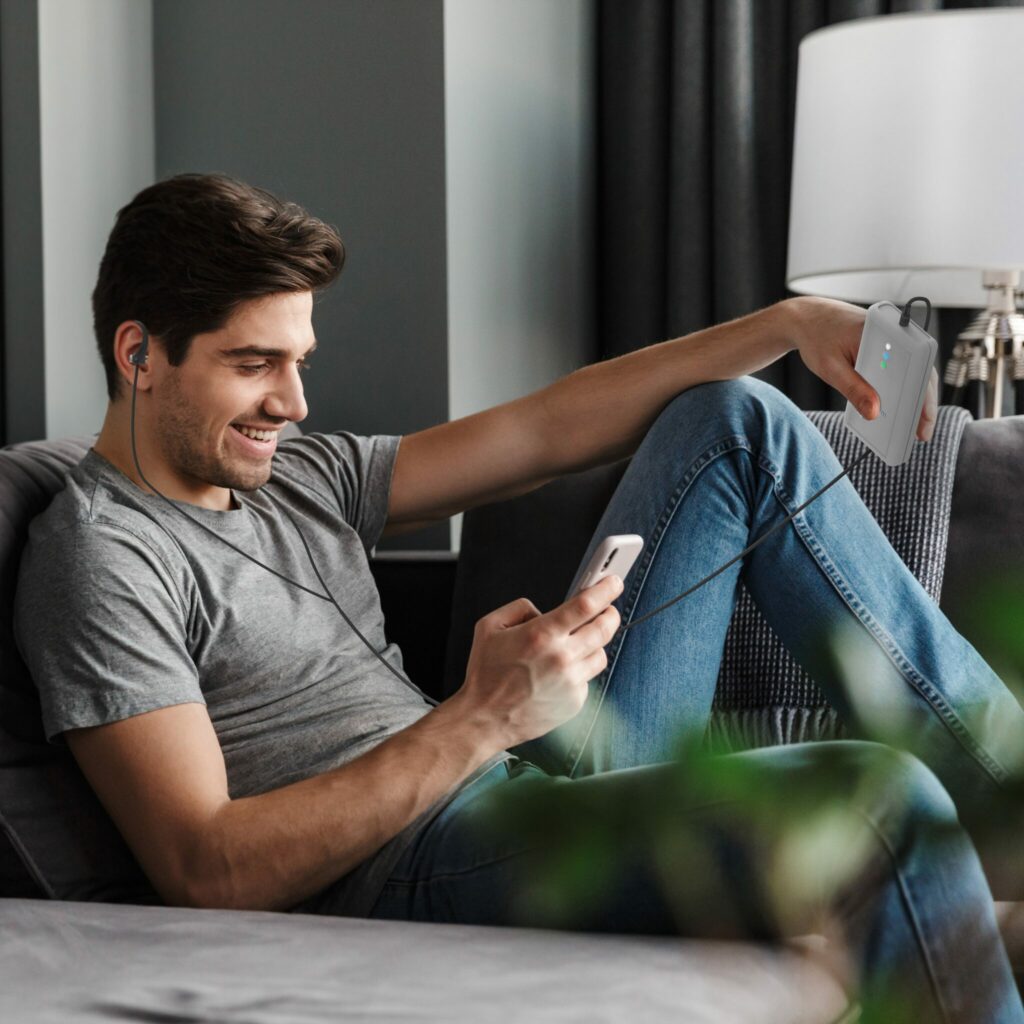


Designed and manufactured with medical device standards: ISO 13485

20+ Clinical Study

6 Patent-Pending
Our Solution: Sending Safe Electrical Pulses Through Ear
Vagustim develops a wearable med-tech device that focuses on non-invasive bilateral auricular vagus nerve stimulation (VNS). VNS is a clinically approved, safe, and effective neuromodulation method*. Since stimulation of the vagus nerve rebalances autonomic nervous system activities, this process enables Vagustim to eliminate and treat autonomic dysfunction-triggered conditions, disorders, and diseases by increasing the activity of parasympathetic nervous system activities.
* Redgrave J, Day D, Leung H, Laud PJ, Ali A, Lindert R, Majid A. Safety and tolerability of Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve stimulation in humans; a systematic review. Brain Stimul. 2018 Nov-Dec;11(6):1225-1238. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2018.08.010. Epub 2018 Aug 23. PMID: 30217648.
Our Research Partners

