Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation for the Treatment of Nervous System Diseases
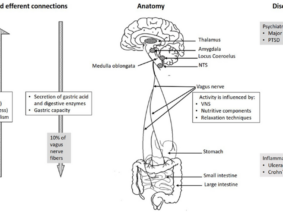
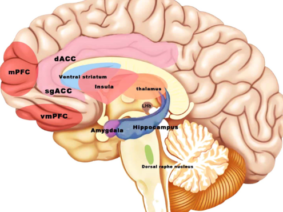
The key findings of the research on Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation for the treatment of nervous system diseases include its potential effectiveness in conditions such as cerebral ischemia , stroke , upper limb function improvement after stroke , sensory recovery in chronic stroke poststroke motor recovery , autism spectrum disorders , schizophrenia , associative memory enhancement in older individuals , learning of novel letter-sound relationships in adults , and modulation of brainstem activity and connectivity in migraine patients . Furthermore, this research has delved into the anatomical advancements of the auricular vagus nerve, treatments for nervous system diseases, and the current state of research on stimulation parameters, providing a basis for further research.
Auricular vs. Traditional Vagus Nerve Stimulation
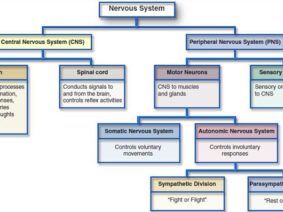
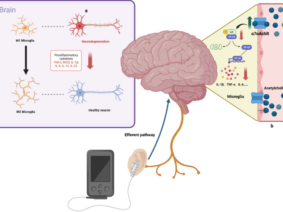
A significant departure from traditional Vagus Nerve Stimulation lies in aVNS’s non-invasiveness. Unlike the surgical implantation necessary for traditional VNS, aVNS offers a non-invasive approach. It specifically targets the auricular branch of the vagus nerve, situated in the external ear, as opposed to the cervical branch affecting the neck and chest. Moreover, aVNS demonstrates fewer side effects and is more cost-effective. However, further exploration is vital to comprehend its comparative effectiveness against traditional Vagus Nerve Stimulation fully.
aVNS vs. Other Non-Invasive Neuroregulation Techniques
In comparison to other non-invasive neuroregulation techniques, aVNS presents distinct advantages. Its non-invasiveness ensures safety and accessibility, setting it apart from invasive methods like deep brain stimulation. Targeting the auricular branch extends its potential in treating various neurological conditions, showcasing promise in stroke recovery, chronic stroke sensory restoration, and migraine management. Nonetheless, extensive research is warranted to directly compare aVNS’s effectiveness with other non-invasive techniques across a broader spectrum of neurological disorders.
Future Implications of aVNS Research
The implications of Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation research are far-reaching for neuroregulation technology and neurological disorder treatments. Its non-invasive nature could usher in safer, more accessible treatments for a wider patient demographic. Further optimization of stimulation parameters might lead to personalized approaches tailored to specific neurological conditions, enhancing efficacy and reducing adverse effects. Furthermore, the ongoing exploration of the auricular vagus nerve’s anatomical and physiological aspects could drive innovative therapeutic strategies for neurological disorders.
References:
Yang, J. E., & Jia, N. (2023). Advances of Research on Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation for Treatment of Nervous System Diseases. Journal of Biosciences and Medicines, 11, 1-14. https://doi.org/10.4236/jbm.2023.114001