Autonomic Dysfunction
Autonomic dysfunction diseases, characterized by an imbalance in the autonomic nervous system, can greatly impact a person’s quality of life. These conditions, including dysautonomia, postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS), and neurocardiogenic syncope, often present with a range of symptoms such as dizziness, rapid heart rate, and low blood pressure. Traditional treatment options have shown limited effectiveness, leaving patients seeking alternative solutions.
Vagus Stimulation: A Promising Therapy for Autonomic Dysfunction
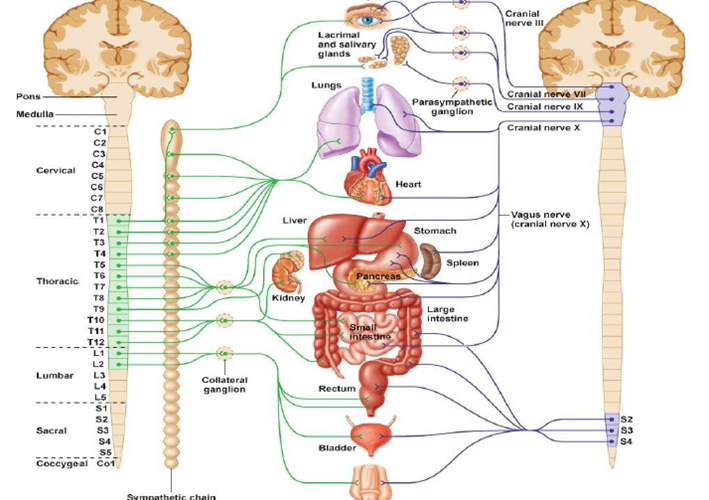
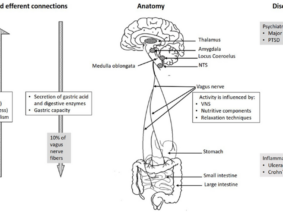
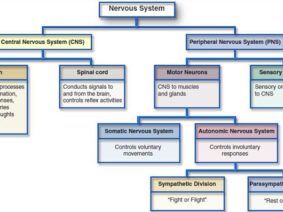
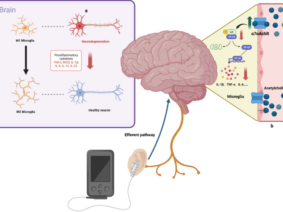
In recent years, vagus nerve stimulation has emerged as a promising therapy for autonomic dysfunction diseases. The vagus nerve, a vital component of the parasympathetic nervous system, controls various bodily functions, including heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and inflammation. By modulating the activity of the vagus nerve, researchers have discovered a potential avenue for managing autonomic dysfunction.
Vagus nerve stimulation involves the use of a small device that delivers electrical impulses to the vagus nerve, either through an implanted device or a non-invasive approach. The electrical stimulation acts as a neuromodulator, influencing the signals transmitted along the vagus nerve and subsequently affecting the autonomic nervous system.
One of the key advantages of vagus stimulation is its ability to regulate the autonomic nervous system without relying on pharmaceutical interventions. This approach holds significant promise, particularly for patients who have not responded well to medication or who wish to minimize their reliance on drugs.
Studies have shown promising results in the application of vagus stimulation for autonomic dysfunction diseases. Patients who received vagus nerve stimulation reported improvements in symptoms such as reduced heart rate variability, decreased blood pressure fluctuations, and increased overall well-being. Additionally, some individuals experienced relief from associated symptoms like headaches, gastrointestinal disturbances, and cognitive impairments.
How Vagus Stimulation Works
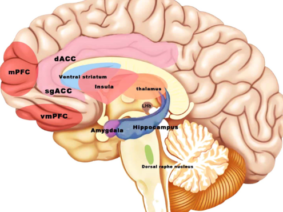
The precise mechanisms by which vagus stimulation exerts its therapeutic effects are still being elucidated. However, researchers believe that the stimulation modulates the release of neurotransmitters, such as norepinephrine and serotonin, which play essential roles in autonomic regulation. Furthermore, vagus stimulation has been shown to influence inflammatory responses, which are often dysregulated in autonomic dysfunction diseases.
In conclusion, vagus stimulation represents a groundbreaking therapeutic approach for autonomic dysfunction diseases. By targeting the autonomic nervous system through electrical stimulation of the vagus nerve, this innovative therapy offers hope for improved symptom management and enhanced quality of life. As research continues and technology advances, vagus stimulation may well become a standard and effective treatment option for those affected by autonomic dysfunction.